
WHO Patient Safety Goals for Emergency Care
The WHO has some goals to promote patient safety. There are the National Patient Safety Goals organised by established organisations like the Joint Commission International (JCI). The following goals are essential for emergency care.
- Correct patient identification
- Effective communication
- Safe medication practices
- Prevent infection
- Reduce harm from high-risk situations
The Swiss cheese model of safety, developed by James Reason, is a risk analysis framework that illustrates how accidents occur when multiple layers, like slices of Swiss cheese, have holes (weakness) that align, allowing a hazard to pass through and cause an incident.
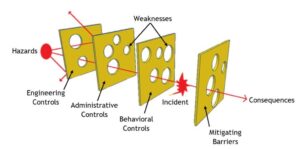
In this model, the slice of Swiss cheese is symbolic of a given measure taken to minimise risk. Each slice is like a line of defence against an incident. The four layers of failures were described by HFACS as
1. Unsafe Acts
2. Preconditions for Unsafe Acts
3. Unsafe Supervision
4. Organisational influences
In healthcare, each slice represents the defence integrated into the design of a system, that are designed to prevent patient safety errors from occurring. Hence, staff should act as barriers, not holes.

